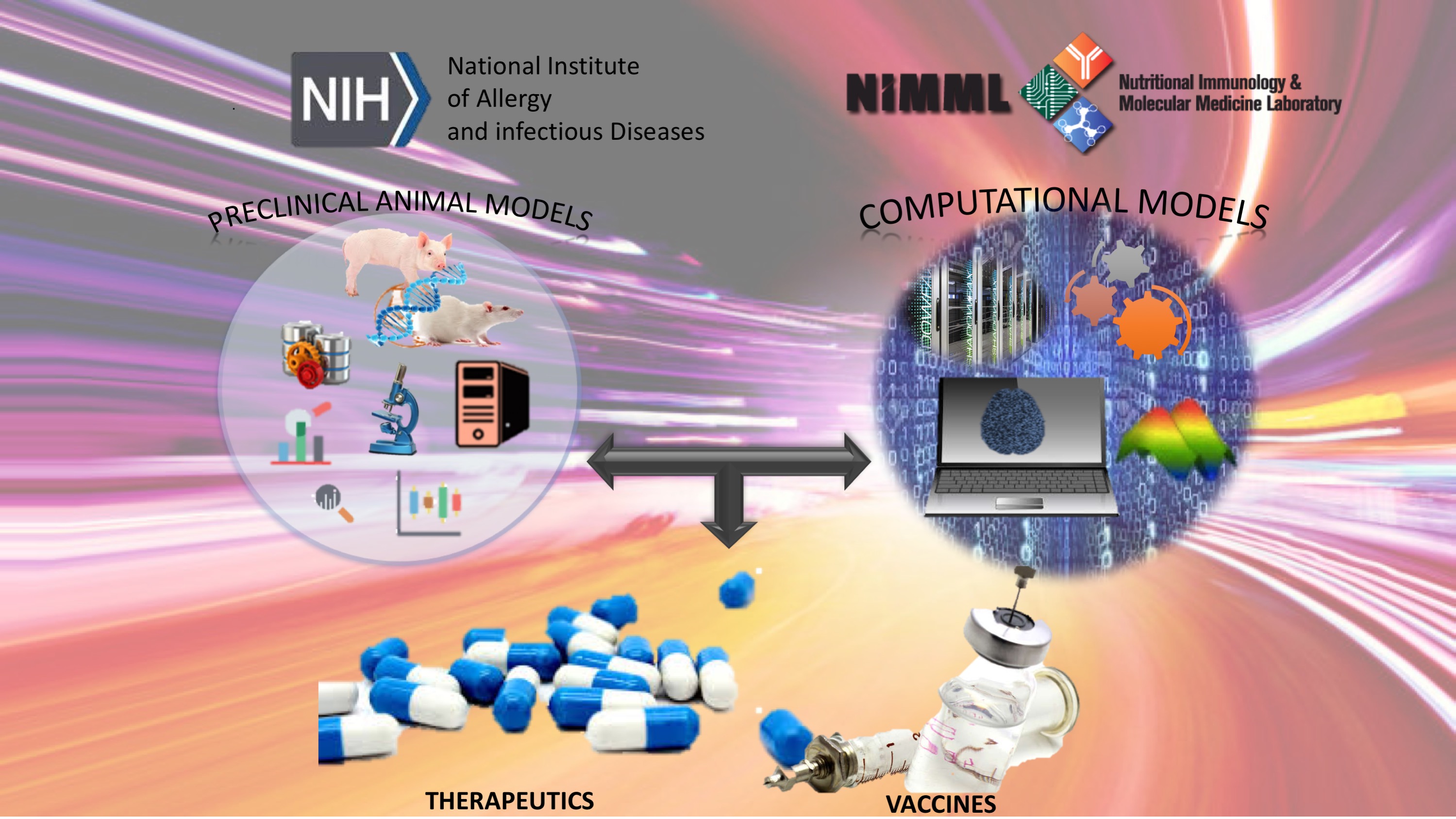
APMEP is a $40-million NIH/NIAID IDIQ contract with the goal to develop alternative preclinical models of enteric pathogens. Through task orders, the contract establishes collaborations between NIMML and biotech and biopharma companies to accelerate the development of novel therapeutics, vaccines and diagnostics for enteric infections.
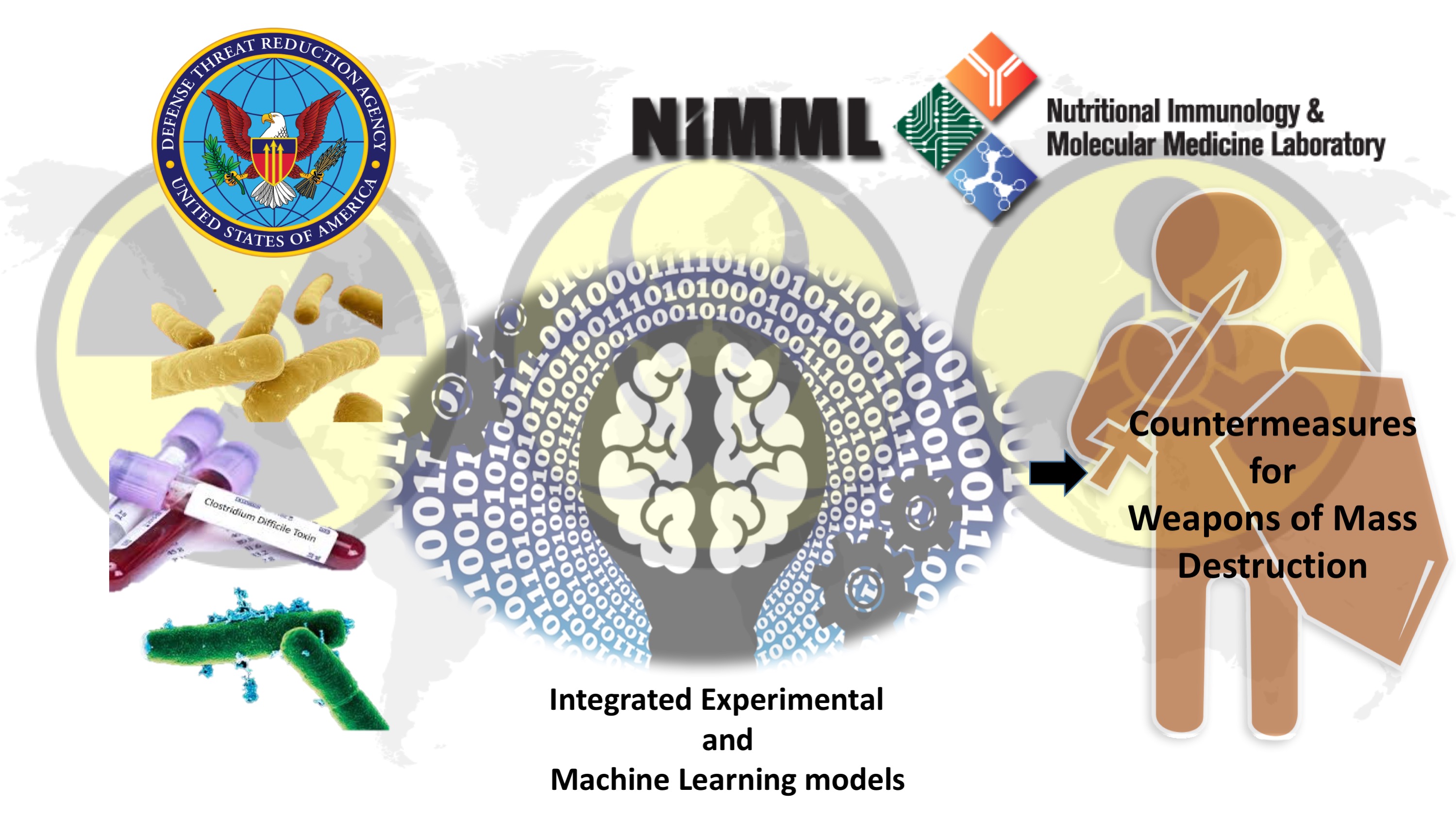
MIDK is a $1.7-million DTRA grant that aims to leverage the power of computational modeling and advanced machine learning methods to model infectious disease kinetics. The ultimate goal of the project is to accelerate the development of effective countermeasures for people exposed to harmful pathogens or their toxins.

MIEP is a $12-million NIAID-funded program at the interface of advanced computational modeling and preclinical, translational and clinical research. MIEP is focused on the development and dissemination of computational models and tools for the studying immunoregulatory mechanisms underlying mucosal immune responses to enteric pathogens.